Fasting For Weight Loss – Addressing The Root Cause Of Weight Gain
In today’s world, where convenience and instant gratification are everything, fasting for weight loss is shunned in favor of pills and potions. However, fasting addresses the root cause of undesirable weight gain, inflammation-induced hormone resistance.
Fasting results in autophagy. Autophagy removes the senescent cells that drive chronic inflammation. This chronic inflammation ultimately leads to hormone resistance. In the case of weight gain, insulin resistance and leptin resistance are the underlying cause. Removing inflammation at the cellular level allows hormones associated with metabolism to function properly, making it possible to finally lose weight.1
Fasting For Weight Loss Comes Down To Dealing With Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation occurs due to factors such as poor diet, stress, toxins, microbiome dysfunction, and undesirable epigenetic expression. Chronic inflammation wreaks havoc on our bodies and leads to various health issues, including weight gain.2
Read more about inflammation and weight gain.
The 3-Legged Stool Of Disease
To visualize the factors that contribute to chronic inflammation, I like to use the analogy of a 3-legged stool. Each leg represents a key component that, when combined, leads to the perfect storm for developing hormone resistance that makes it impossible to lose weight.
Leg 1: Stressors
The first leg of the stool is made up of various stressors that trigger inflammation. These stressors include a poor diet, heavy metal toxicity, emotional stress, exposure to mold and pollution, underlying infections, and harmful chemicals found in everyday products. While these stressors may seem unrelated, they all contribute to inflammation and hormone resistance.3
Leg 2: Gut Health
The second leg of the stool focuses on gut health, specifically the microbiome. The microbiome is a collection of microorganisms that live in our intestines and play a crucial role in our overall health. When the microbiome is imbalanced, or dysbiosis occurs, it leads to inflammatory conditions. Therefore, addressing and correcting microbiome dysbiosis is essential to losing weight.4
Fasting Improves Microbiome Health
Fasting has a positive impact on the diversity of our microbiome. A microbiome lacking diversity is linked with obesity.5
Following an intermittent fasting pattern increases the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). Not only do these SCFAs play a crucial role in gut health, but they also possess anti-inflammatory properties.6
Fasting assists beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which play important roles in digestion. Fasting also increases the number of Bacteroides fragilis. Bacteroides fragilis is linked to the production of regulatory T cells (tReg cells), which are essential for maintaining a healthy immune system and preventing unchecked inflammation.7 These beneficial bacteria reduce the growth of Clostridium, a bacteria that causes us harm.8
Fasting improves the function of the gut barrier by increasing zonulin production. By increasing levels of this crucial protein, fasting strengthens our gut barrier, effectively reducing inflammation that stems from leaky gut.9
Leg 3: Gene Expression
The third and final leg of the stool revolves around gene expression. While our DNA remains constant, the genes that are expressed change based on various factors such as lifestyle, stressors, and microbiome health. Detrimental gene expression plays a significant role in uncontrolled inflammation, making it crucial to optimize epigenetic expression for weight loss. Studies have found that fasting leads to alterations in the expression of genes involved in metabolism, inflammation, and aging.10
Diet Is Only One Small Aspect Of Losing Weight
As we can see, diet is just one small aspect when it comes to losing weight. To put an end to chronic inflammation, we must address all three legs of the stool and work towards a holistic approach to improving our overall health. The key is to stop inflammation, which in turn puts an end to hormone resistance.11
Read more about the 3-Legged Stool.
Insulin Resistance
When our bodies are in a state of chronic inflammation, it naturally leads to insulin resistance. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels and plays a crucial role in metabolism. When our body becomes resistant to insulin, it results in weight gain as the excess glucose is stored as fat instead of being used for energy.12
Read more about insulin resistance.
Leptin Resistance
Leptin is a hormone produced by fat cells that plays an important role in regulating energy balance and body weight. It acts on the hypothalamus, the part of our brain that controls hunger and metabolism, to signal when we are full and should stop eating.
However, just like with other hormones in the body, there can be issues with leptin signaling that can lead to leptin resistance. This means that even if our body is producing enough leptin, our brain is not sensing it properly and we may not feel full or satisfied after eating. There are a few potential causes of leptin resistance, but the most common is chronic inflammation.13
Read more about leptin resistance.
What Is Causing Hormone Resistance That Leads To Weight Gain?
Hormone resistance occurs when our bodies become desensitized to the signals of certain hormones. Hormone resistance takes place when hormones are unable to dock to cellular membrane receptors due to cellular membrane inflammation. The reason for this is because inflammation changes the shape of the cellular membrane receptors. If hormones can’t dock to receptors, they can’t relay their message into cells. When this happens, cells are unable to take instructions. One side effect of this is undesirable weight gain.14 15
Fasting For Weight Loss – A Solution For Inflammation And Hormone Resistance
Fasting is a powerful tool in addressing both inflammation and hormone resistance. By giving our bodies a break from constant food consumption, we can reduce inflammation and allow our cells to heal. During fasting, our bodies produce less insulin, which helps decrease insulin resistance and allows us to burn stored fat for energy.16
Furthermore, fasting has been shown to improve hormone sensitivity. Studies have found that intermittent fasting decreases leptin levels, making our bodies more sensitive to its signals and helping to reduce appetite and promote weight loss.17
How Fasting Reduces Inflammation
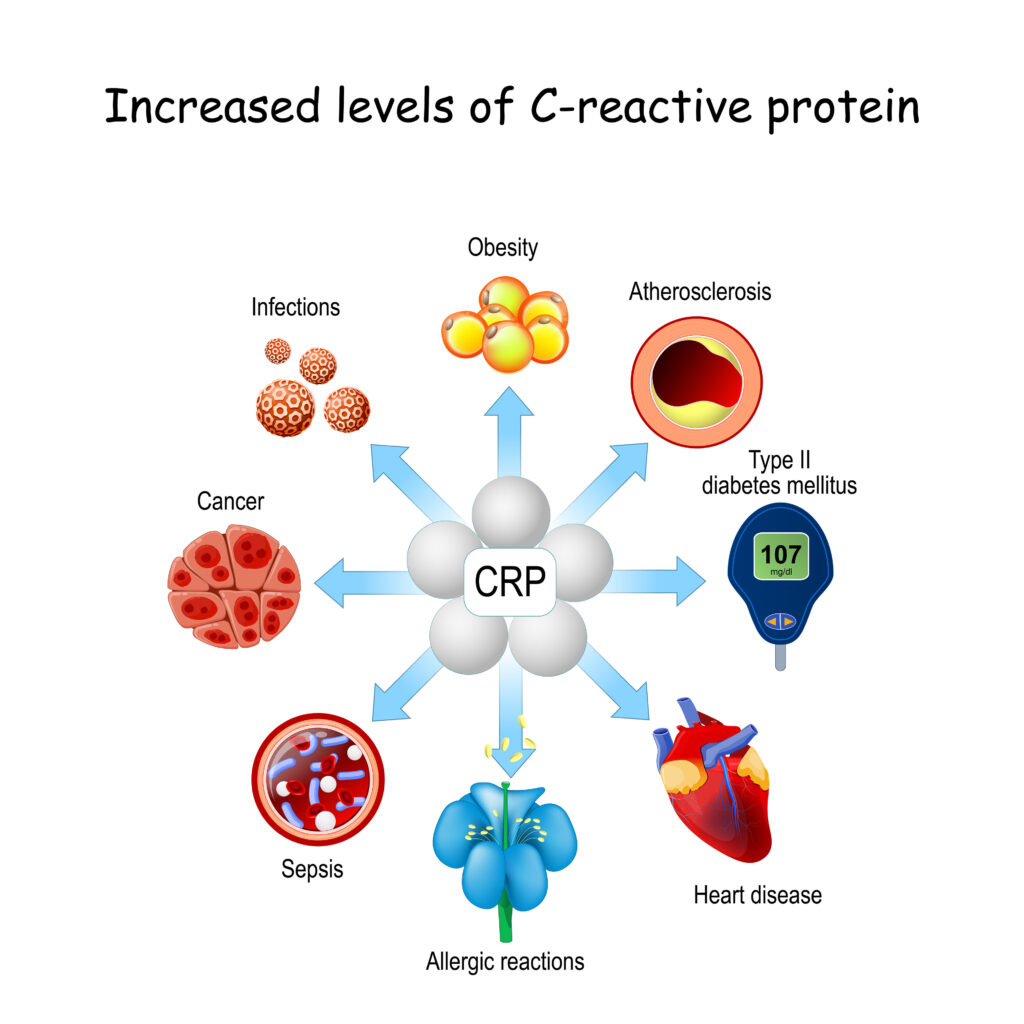
Fasting has shown to have a positive impact on reducing the production of inflammatory markers in the body, specifically C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). These two markers are closely associated with chronic inflammation and hormone resistance.18
In a recent 2024 study, researchers identified another reason why fasting has been shown to exhibit its anti-inflammatory effects. The discovery centers around a molecule called arachidonic acid (AA), which has been found to increase during periods of fasting. Upon further investigation, scientists have found that AA plays a crucial role in inhibiting the activities of a protein complex known as NLRP3 inflammasome, which is responsible for triggering inflammation in the body.19
A 2019 study found that intermittent fasting has the ability to significantly decrease the amount of inflammation-causing monocytes. This reduction in monocytes led to a noticeable decrease in overall inflammation levels.20
Research has shown that fasting for more than 24 hours lowers cellular oxidative stress. This is because fasting leads to a decrease in reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. ROS are a type of free radical that causes significant damage to cells if not kept in check. By reducing their production, fasting helps to reduce the overall oxidative stress levels in the body.21
Fasting has also been found to increase the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase and catalase. These enzymes play a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals and preventing damage to cells. With increased activity, these enzymes can more effectively combat oxidative stress and protect cells from damage.22
Intermittent Fasting For Weight Loss
Intermittent fasting is a popular method of fasting where one alternates between periods of eating and fasting. This approach can be tailored to fit individual lifestyles and preferences.
By giving our bodies a break from constant food consumption, intermittent fasting allows our bodies to heal and reset, leading to reduced inflammation and improved hormone sensitivity. This, in turn, leads to weight loss and overall health improvements.23
5 Day Fasting For Weight Loss
A 5-day water fast is just what it sounds like, one only consumes water for five days. This extended period of fasting, allows the body to heal and repair on a deeper level.
During this type of fast, the body goes into a state of autophagy, where it breaks down and recycles old and damaged cells like senescent cells. This process reduces inflammation, improves hormone sensitivity, and leads to weight loss. A 5-day water fast also corresponds with an increase in growth hormone and promotes the release of stem cells that regenerate tissue.24 25 26
According to recent research, individuals who were overweight and underwent multiple 5-day water fasts during a span of six months experienced an 8% decrease in their body weight on average.27
Read about how to balance out fasting with feasting for optimal health.
Fasting For Weight Loss – Addressing The Root Cause Of Weight Gain
Fasting is a powerful tool that addresses the root cause of weight gain, inflammation-induced hormone resistance. By incorporating fasting into our lifestyles, we can reduce chronic inflammation, improve insulin and leptin sensitivity, and ultimately achieve sustainable weight loss.
Read more about fat loss hormones.
References
1 Pahwa R, Goyal A, Jialal I. Chronic Inflammation. [Updated 2023 Aug 7]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493173/
2 Fahed G, Aoun L, Bou Zerdan M, Allam S, Bou Zerdan M, Bouferraa Y, Assi HI. Metabolic Syndrome: Updates on Pathophysiology and Management in 2021. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 12;23(2):786. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020786. PMID: 35054972; PMCID: PMC8775991.
3 Kharrazian D. Exposure to Environmental Toxins and Autoimmune Conditions. Integr Med (Encinitas). 2021 Apr;20(2):20-24. PMID: 34377090; PMCID: PMC8325494.
4 Khan MN, Khan SI, Rana MI, Ayyaz A, Khan MY, Imran M. Intermittent fasting positively modulates human gut microbial diversity and ameliorates blood lipid profile. Front Microbiol. 2022 Aug 23;13:922727. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.922727. PMID: 36081793; PMCID: PMC9445987.
5 Aoun A, Darwish F, Hamod N. The Influence of the Gut Microbiome on Obesity in Adults and the Role of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics for Weight Loss. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2020 Jun 30;25(2):113-123. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2020.25.2.113. PMID: 32676461; PMCID: PMC7333005.
6 Medawar, E., Haange, SB., Rolle-Kampczyk, U. et al. Gut microbiota link dietary fiber intake and short-chain fatty acid metabolism with eating behavior. Transl Psychiatry 11, 500 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-021-01620-3
7 Cheng H, Guan X, Chen D, Ma W. The Th17/Treg Cell Balance: A Gut Microbiota-Modulated Story. Microorganisms. 2019 Nov 20;7(12):583. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7120583. PMID: 31756956; PMCID: PMC6956175.
8 Angoorani P, Ejtahed HS, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Siadat SD, Soroush AR, Larijani B. Gut microbiota modulation as a possible mediating mechanism for fasting-induced alleviation of metabolic complications: a systematic review. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2021 Dec 14;18(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s12986-021-00635-3. PMID: 34906176; PMCID: PMC8670288.
9 Fasano A. All disease begins in the (leaky) gut: role of zonulin-mediated gut permeability in the pathogenesis of some chronic inflammatory diseases. F1000Res. 2020 Jan 31;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-69. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.20510.1. PMID: 32051759; PMCID: PMC6996528.
10 Stylianou E. Epigenetics of chronic inflammatory diseases. J Inflamm Res. 2018 Dec 20;12:1-14. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S129027. PMID: 30588059; PMCID: PMC6304253.
11 Straub RH. Interaction of the endocrine system with inflammation: a function of energy and volume regulation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Feb 13;16(1):203. doi: 10.1186/ar4484. PMID: 24524669; PMCID: PMC3978663.
12 Barazzoni R, Gortan Cappellari G, Ragni M, Nisoli E. Insulin resistance in obesity: an overview of fundamental alterations. Eat Weight Disord. 2018 Apr;23(2):149-157. doi: 10.1007/s40519-018-0481-6. Epub 2018 Feb 3. PMID: 29397563.
13 Longo, V. D., & Mattson, M. P. (2014). Fasting: molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Cell metabolism, 19(2), 181–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.12.008
14 Majeed S, Ahmad AB, Sehar U, Georgieva ER. Lipid Membrane Mimetics in Functional and Structural Studies of Integral Membrane Proteins. Membranes (Basel). 2021 Sep 3;11(9):685. doi: 10.3390/membranes11090685. PMID: 34564502; PMCID: PMC8470526.
15 Ammendolia, D.A., Bement, W.M. & Brumell, J.H. Plasma membrane integrity: implications for health and disease. BMC Biol 19, 71 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-021-00972-y
16 Barnosky AR, Hoddy KK, Unterman TG, Varady KA. Intermittent fasting vs daily calorie restriction for type 2 diabetes prevention: a review of human findings. Transl Res. 2014 Oct;164(4):302-11. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2014.05.013. Epub 2014 Jun 12. PMID: 24993615.
17 Mendoza-Herrera K, Florio AA, Moore M, Marrero A, Tamez M, Bhupathiraju SN, Mattei J. The Leptin System and Diet: A Mini Review of the Current Evidence. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 24;12:749050. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.749050. PMID: 34899599; PMCID: PMC8651558.
18 Mulas A, Cienfuegos S, Ezpeleta M, Lin S, Pavlou V, Varady KA. Effect of intermittent fasting on circulating inflammatory markers in obesity: A review of human trials. Front Nutr. 2023 Apr 17;10:1146924. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1146924. PMID: 37139450; PMCID: PMC10149732.
19 Pereira, M., Liang, J. J., Edwards-Hicks, J., Meadows, A. M., Hinz, C., Liggi, S., Hepprich, M., Mudry, J. M., Kim, H., Griffin, J. L., Fraser, I. D. C., Sack, M. N., Hess, C., & Bryant, C. E. (2024). Arachidonic acid inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome is a mechanism to explain the anti-inflammatory effects of fasting. Cell Reports, 43(2), 113700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2024.113700
20 Jordan, S., & Tung, N. (2019, August 22). Dietary intake regulates the circulating inflammatory monocyte pool: Cell. https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(19)30850-5
21 Motori, E., & Puyal, J. (2013, December 13). Inflammation-Induced Alteration of Astrocyte Mitochondrial Dynamics Requires Autophagy for Mitochondrial Network Maintenance: Cell. https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(13)00454-3
22 Ahn JH, Shin BN, Song M, Kim H, Park JH, Lee TK, Park CW, Park YE, Lee JC, Yong JH, Lee CH, Hwang IK, Won MH, Lee YL. Intermittent fasting increases the expressions of SODs and catalase in granule and polymorphic cells and enhances neuroblast dendrite complexity and maturation in the adult gerbil dentate gyrus. Mol Med Rep. 2019 Mar;19(3):1721-1727. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.9822. Epub 2019 Jan 4. PMID: 30628688; PMCID: PMC6390044.
23 Ganesan K, Habboush Y, Sultan S. Intermittent Fasting: The Choice for a Healthier Lifestyle. Cureus. 2018 Jul 9;10(7):e2947. doi: 10.7759/cureus.2947. PMID: 30202677; PMCID: PMC6128599.
24 Antunes F, Erustes AG, Costa AJ, Nascimento AC, Bincoletto C, Ureshino RP, Pereira GJS, Smaili SS. Autophagy and intermittent fasting: the connection for cancer therapy? Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2018 Dec 10;73(suppl 1):e814s. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2018/e814s. PMID: 30540126; PMCID: PMC6257056.
25 Ho KY, Veldhuis JD, Johnson ML, Furlanetto R, Evans WS, Alberti KG, Thorner MO. Fasting enhances growth hormone secretion and amplifies the complex rhythms of growth hormone secretion in man. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):968-75. doi: 10.1172/JCI113450. PMID: 3127426; PMCID: PMC329619.
26 Wu, S. (2018, February 5). Fasting triggers stem cell regeneration of damaged, old immune system. USC News. https://news.usc.edu/63669/fasting-triggers-stem-cell-regeneration-of-damaged-old-immune-system/
27 Heilbronn LK, de Jonge L, Frisard MI, et al. Effect of 6-month calorie restriction on biomarkers of longevity, metabolic adaptation, and oxidative stress in overweight individuals: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006;295(13):1539-1548.