Symptoms Of Autoimmune Disease – How To Know If You Suffer From Autoimmune Conditions
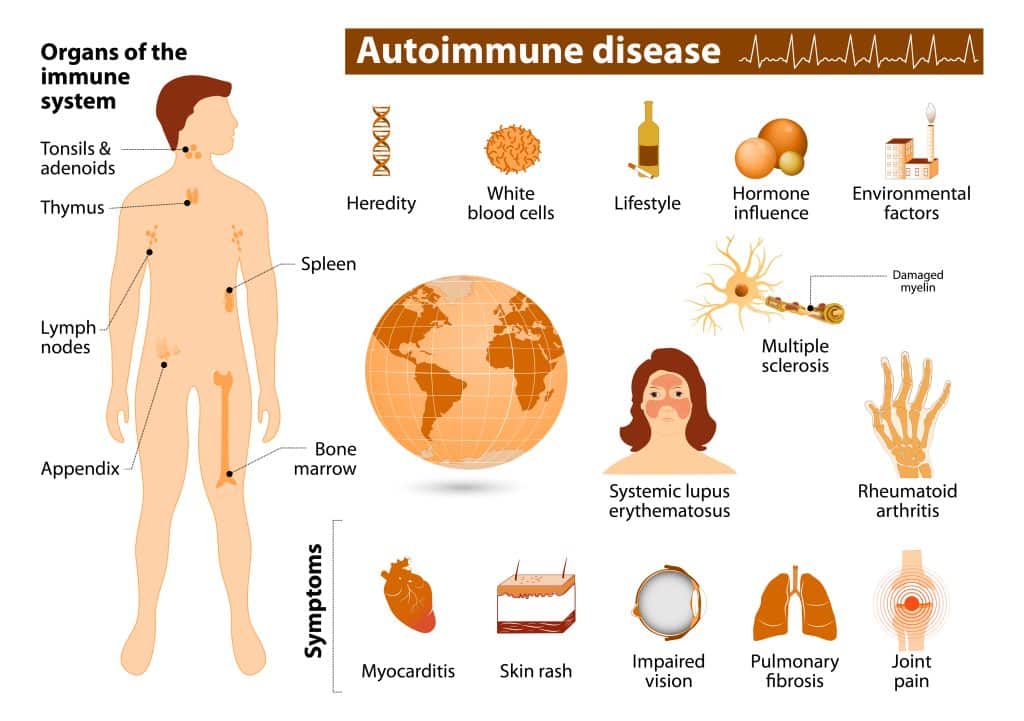
There are many symptoms of autoimmune disease. Autoimmune conditions occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy tissues, cells, or organs. Knowing if you have an autoimmune condition can be difficult to determine. Let’s take a look at the symptoms of autoimmune disease, its causes, diagnosis, and treatment.
Autoimmune conditions occur due to different factors, such as genes and environmental triggers like infections or inflammation. It’s important to note that while some autoimmune conditions may be hereditary, not all are.
Common symptoms include:
• Fatigue and general tiredness
• Joint pain or swelling
• Skin rashes or lesions
• Unexplained fever or body aches
• Stiffness in the joints and muscles
• Digestive issues like diarrhea, constipation, gas, or bloating
• Poor concentration and difficulty focusing
• Lowered appetite or general malaise
• Weight loss or weight gain without trying
• Rapid breathing or heart rate
• Excessive sweating or heat intolerance
• Anemia (low levels of red blood cells)
• Low blood pressure when standing up quickly
While these symptoms can be caused by other health conditions as well, they may indicate an underlying autoimmune condition if other causes have been ruled out.1 2
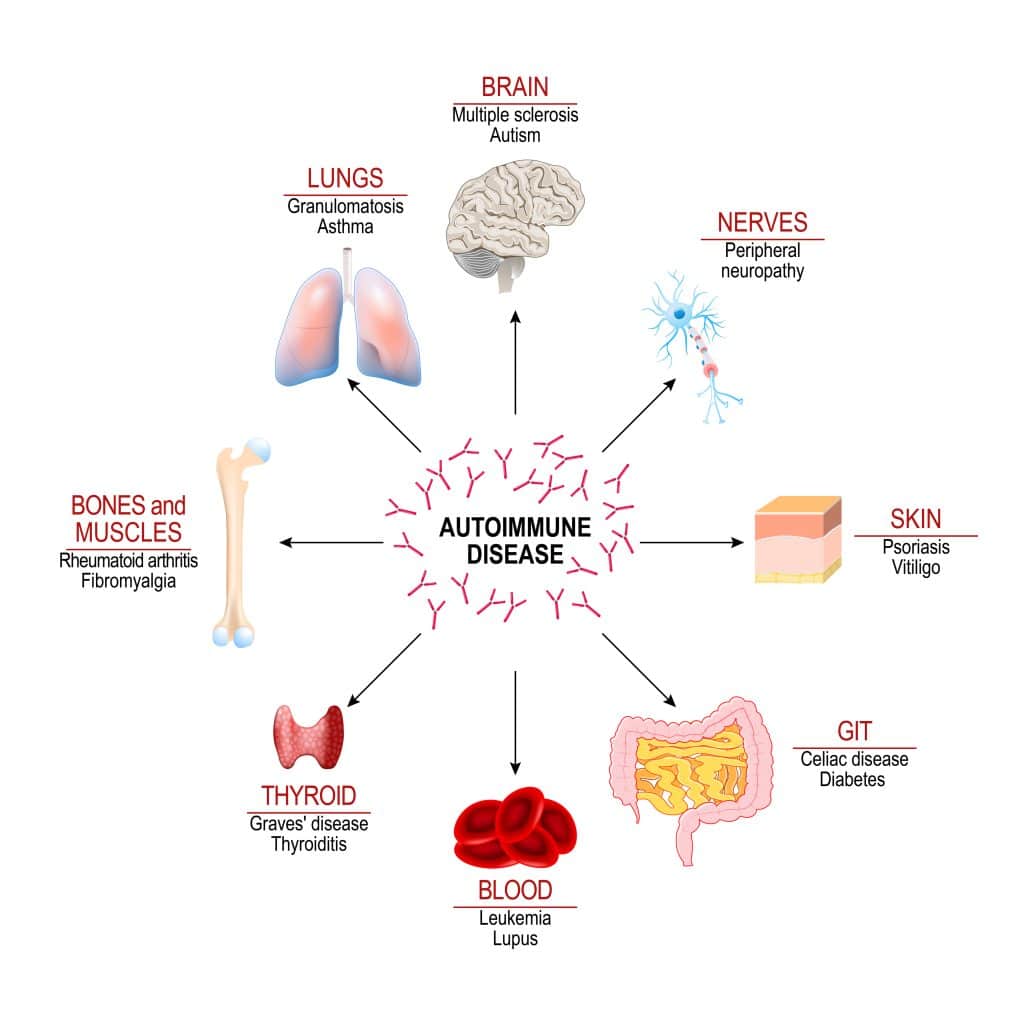
Common Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases are conditions that cause the body’s immune system to attack its own healthy tissue. Common examples of autoimmune diseases include:
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting the joints, resulting in pain, swelling, stiffness, and joint damage. Other symptoms may include fatigue and anemia.3
Read more about Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) commonly known as lupus, is an inflammatory disorder that can affect multiple organs and systems throughout the body. It can cause joint pain, swelling, skin rashes, and other symptoms.4
Read more about Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a neurological disease that affects communication between the brain and other parts of the body. Symptoms can include vision problems, difficulty in walking and balance, muscle weakness or spasms, and cognitive issues.6
Read more about Multiple Sclerosis.
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune condition that affects the thyroid gland. It causes an overproduction of the hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine, leading to weight loss, increased appetite, sensitivity to heat, insomnia, and an enlarged thyroid gland, known as a goiter.7
Read more about Graves’ disease.
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that causes red, scaly patches of skin. It can occur anywhere on the body but is most common on the elbows, knees, scalp, hands, and feet. It may also cause joint pain and swelling.8
Read more about Psoriasis.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is an umbrella term that includes two chronic inflammatory disorders of the gastrointestinal tract: Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Symptoms include abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, weight loss, fatigue, and malnutrition.9
Read more about Inflammatory Bowel Disease.

Leaky Gut Syndrome affects the gastrointestinal tract and causes a breakdown in the intestinal wall that allows undigested food particles to enter the bloodstream and trigger an immune response. Symptoms of Leaky Gut Syndrome include abdominal pain and cramping, bloating, gas, diarrhea or constipation, food sensitivities, and fatigue. Treatment includes dietary changes, probiotics supplements, and lifestyle modifications.10
Read more about Leaky Gut Syndrome.
Addison’s disease is caused by a decrease in the production of hormones from the adrenal glands. Symptoms of Addison’s disease include fatigue, weight loss, low blood pressure, darkening of the skin due to increased pigmentation, and salt cravings. Treatment includes hormone replacement therapy with corticosteroids.11
Read more about Addison’s disease.
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorder that affects the thyroid gland. Symptoms include fatigue, dry skin, constipation, joint pain, and sensitivity to cold temperatures. Treatment typically includes hormone replacement therapy and medications such as levothyroxine to restore normal thyroid function. It is important to note that Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis can also cause infertility in women if left untreated.12
Read more about Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis.
Celiac Disease is another autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues. It is caused by an intolerance to gluten, a protein found in wheat, rye, and barley. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloating, gas, weight loss or gain, and fatigue. Treatment involves adhering to a strict gluten-free diet.13
Read more about Celiac Disease.
Symptoms Of Autoimmune Disease – Genes
Autoimmune diseases are complex conditions that have been linked to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Many autoimmune diseases have a strong hereditary component, which means that they can be passed down through families. For example, if someone in your family has an autoimmune disease, you may be more likely to develop the same or a similar condition.
Research suggests that certain genes can make people more likely to develop autoimmune diseases.14 However, genes alone don’t cause these conditions, as environmental factors such as infections, toxins, and medications can trigger an autoimmune response.
Symptoms Of Autoimmune Disease – Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as exposure to certain toxins or infectious agents can also contribute to the development of autoimmune disease. Exposure to certain types of chemicals, including heavy metals, herbicides, pesticides, and solvents, has been linked to an increased risk of developing some autoimmune diseases.15 16 17
Read more about common toxins we are exposed to.
Infections caused by certain viruses and bacteria have been shown to trigger the onset of some autoimmunity. The Epstein-Barr virus, for example, is associated with multiple autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjögren’s syndrome.18
Additionally, infections caused by certain parasites have been linked to an increased risk of developing immune-mediated conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis.19 Finally, it is thought that the environment may also play a role in modulating existing autoimmune processes. Stress and dietary changes are other environmental factors thought to influence the course of certain autoimmunity conditions.20
Treating Autoimmune Disease – Reducing Toxin Exposure
One of the most important steps in treating autoimmune disease is to reduce exposure to toxins. These toxins can come from a variety of sources, including environmental chemicals, industrial pollutants, and even certain foods. To protect yourself from these potential hazards, it is important to be aware of where you are exposed and how you can reduce those exposures.
First, limit exposure to environmental chemicals and pollutants. This may include avoiding areas where air pollution is high, such as near busy highways or industrial sites. It is also important to reduce exposure to household chemicals by using natural cleaning products whenever possible.
Symptoms Of Autoimmune Disease – Mold Exposure
Mold exposure is one of the causes of autoimmune diseases. Mold can cause long-term health problems when it’s present in our environment. This type of fungi releases toxins known as mycotoxins that can harm us and interfere with our immune system once inhaled or touched. When we’re exposed to mycotoxins, it can lead to immune system dysregulation. If you spend time in buildings that are contaminated with mold, this could be the core cause of autoimmune conditions.21 22
Read more about how toxic mold affects our health.
What Causes Autoimmune Diseases – Heavy Metals Like Mercury And Lead
Heavy metals such as mercury and lead have been linked to autoimmune diseases. Exposure to mercury increases the risk of developing autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis.23
Lead is another heavy metal that can accumulate in our environment from lead-based paint, industrial emissions, and contaminated soil. Exposure to lead has been linked to an increased risk of developing autoimmune conditions, inflammatory bowel disease, and psoriasis.24
Both mercury and lead can damage the immune system by causing inflammation, impairing antibody production, and disrupting cell signaling. Reducing exposure to heavy metals is an important step in the prevention of autoimmune diseases.
Read more about how toxic heavy metals cause autoimmune conditions.
Treating Autoimmune Disease – Remove Heavy Metals From The Body With DMSA
Heavy metals, such as lead, mercury, and arsenic, can accumulate in the body over time and contribute to autoimmune diseases. One way to remove heavy metals from the body is by taking a chelating agent, such as DMSA (dimercaptosuccinic acid). DMSA has been used for many years in the medical field to treat lead poisoning and other metal intoxications and is now being used off-label to help remove the toxins that cause autoimmune diseases.
Research suggests that DMSA may help reduce inflammation associated with autoimmune diseases by removing excess heavy metals from the body. Additionally, DMSA helps to restore balance and protect the body’s cells from further damage caused by these toxins.25
Read more about removing heavy metals from the body.
Symptoms Of Autoimmune Disease – Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can help reduce the impact of autoimmune disease. This includes making certain dietary adjustments to minimize inflammation, reducing stress levels, and getting regular exercise.26
When it comes to diet, there are some foods that trigger inflammation in those with autoimmune diseases. These include processed foods, sugar-laden snacks and desserts, and food allergens such as gluten and dairy. Processed foods often contain a lot of preservatives, additives, and other unknown toxins. Eating whole, organic, unprocessed foods will help reduce exposure to these harmful substances.
Replacing these with anti-inflammatory foods and consuming a healthy diet like my Cellular Healing Diet can make a big difference in overall health.
Read more about my Cellular Healing Diet.

Symptoms Of Autoimmune Disease
Symptoms of autoimmune disease vary depending on the type but may include fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, muscle weakness, and more. Treatment usually involves a combination of detox and lifestyle changes that can help reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
Read more about what causes autoimmune conditions.
References
1 Zerbe, Leah. “If You Have These Symptoms, You May Have an Autoimmune Disease.” Dr. Axe, 16 Dec. 2019, draxe.com/health/autoimmune-disease-symptoms/.
2 “What Are Common Symptoms of Autoimmune Disease?” Johns Hopkins Medicine, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/what-are-common-symptoms-of-autoimmune-disease.
3 Rheumatoid arthritis – Symptoms and causes. (2023, January 25). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/rheumatoid-arthritis/symptoms-causes/syc-20353648
4 Lupus symptoms | Lupus Foundation of America. (2023). Lupus Foundation of America. https://www.lupus.org/resources/common-symptoms-of-lupus
6 Multiple sclerosis – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic. (2022, December 24). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/multiple-sclerosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20350269
7 Graves’ disease – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic. (2022, June 14). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/graves-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20356240
8 Psoriasis – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic. (2022, October 8). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/psoriasis/symptoms-causes/syc-20355840
9 What is inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)? | IBD. (2022). https://www.cdc.gov/ibd/what-is-ibd.htm
10 McMillen, M. (2011, July 11). Leaky Gut Syndrome: What Is It? WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/features/leaky-gut-syndrome
11 Addison’s disease – Diagnosis and treatment – Mayo Clinic. (2022, December 8). https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/addisons-disease/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20350296
12 American Thyroid Association. (2020b, June 8). Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis | American Thyroid Association. https://www.thyroid.org/hashimotos-thyroiditis/
13 Celiac Disease. (2023). Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/celiac-disease
14 Scacheri, Cheryl. “Genetic Variation and Disease: GWAS.” Nature News, Nature Publishing Group, www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/genetic-variation-and-disease-gwas-682/.
15 Mueller, Thomas C., et al. “Shikimate Accumulates in Both Glyphosate-Sensitive and Glyphosate-Resistant Horseweed (Conyza CanadensisL. Cronq.).” Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, vol. 51, no. 3, 2003, pp. 680–684., doi:10.1021/jf026006k.
16 Cox, Paul Alan, et al. “Dietary Exposure to an Environmental Toxin Triggers Neurofibrillary Tangles and Amyloid Deposits in the Brain.” Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, vol. 283, no. 1823, 2016, p. 20152397., doi:10.1098/rspb.2015.2397.
17 “What Are Parabens, and Why Don’t They Belong in Cosmetics?” Environmental Working Group, www.ewg.org/what-are-parabens.
18 Houen G, Trier NH. Epstein-Barr Virus and Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 7;11:587380. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.587380. PMID: 33488588; PMCID: PMC7817975.
19 Abu-Shakra M, Shoenfeld Y. Parasitic infection and autoimmunity. Autoimmunity. 1991;9(4):337-44. doi: 10.3109/08916939108997136. PMID: 1954314.
20 Campbell, Jana, and Ulrike Ehlert. “Acute Psychosocial Stress: Does the Emotional Stress Response Correspond with Physiological Responses?” Psychoneuroendocrinology, vol. 37, no. 8, 2012, pp. 1111–1134., doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2011.12.010.
21 Tessier, L. (2020, February 10). Endocrine Impacts of Mycotoxins. Naturopathic Doctor News and Review. https://ndnr.com/endocrinology/endocrine-impacts-of-mycotoxins/
22 Rea WJ, Didriksen N, Simon TR, Pan Y, Fenyves EJ, Griffiths B. Effects of toxic exposure to molds and mycotoxins in building-related illnesses. Arch Environ Health. 2003 Jul;58(7):399-405. doi: 10.1080/00039896.2003.11879140. PMID: 15143852.
23 Pollard KM, Cauvi DM, Toomey CB, Hultman P, Kono DH. Mercury-induced inflammation and autoimmunity. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2019 Dec;1863(12):129299. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2019.02.001. Epub 2019 Feb 10. PMID: 30742953; PMCID: PMC6689266.
24 McFarland, M. J., Hauer, M. E., & Reuben, A. (2022). Half of US population exposed to adverse lead levels in early childhood. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(11). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2118631119
25 Aposhian HV. DMSA and DMPS—water soluble antidotes for heavy metal poisoning. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology. 1983;23:193–215.
26 Trapp EG, Chisholm DJ, Freund J, et al. The effects of high-intensity intermittent exercise training on fat loss and fasting insulin levels of young women. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008;32(4):684-691.




