What Causes High Blood Pressure – Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure
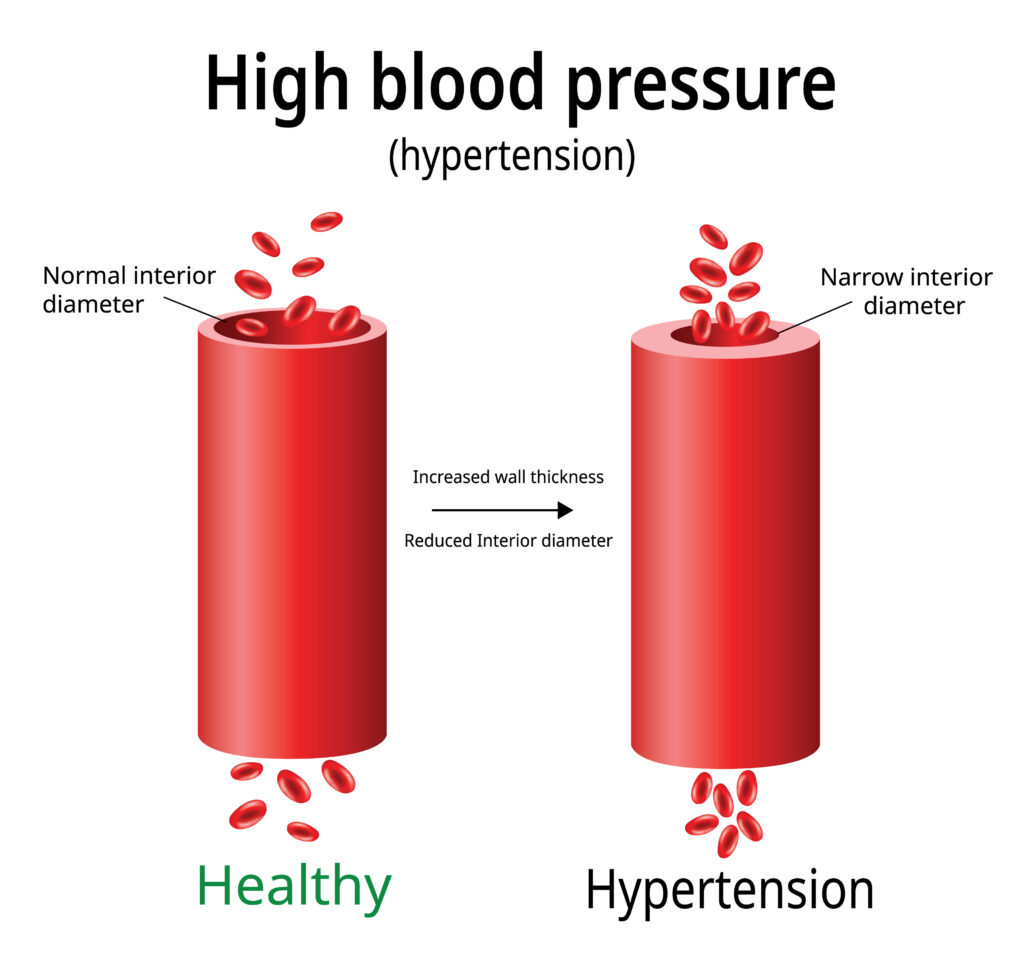
Exactly what causes high blood pressure is a complicated question, as there are so many factors at play. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently too high, putting an extra strain on the heart and blood vessels.
Unhealthy lifestyle habits such as a diet high in refined table salt, a lack of physical activity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption lead to high blood pressure. High blood pressure runs in families so there is a genetic link as well. As we age, our blood vessels become less flexible and narrow, increasing blood pressure.1 2 Chronic stress or certain life events often lead to temporary spikes in blood pressure.3 Not getting enough sleep also results in high blood pressure.4
What Causes High Blood Pressure – Inflammation
Studies have shown the link between chronic inflammation and high blood pressure. When the body is in a state of chronic inflammation, it produces cytokines, which are proteins that promote inflammation. Cytokines affect the development of hypertension in a few different ways. One way is through inflammation, which causes damage to the lining of blood vessels and leads to plaque buildup. This makes it harder for blood to flow through the vessels, increasing blood pressure.
Another way cytokines contribute to hypertension is by causing blood vessels to constrict, making it more difficult for blood to flow through them. In addition, cytokines affect the function of certain hormones involved in regulating blood pressure, such as angiotensin and aldosterone.5
Microbiome Dysfunction Drives The Inflammation Behind High Blood Pressure
Chronic inflammation that is behind high blood pressure is driven by microbiome dysfunction. When the microbiome isn’t adequately diversified and doesn’t contain sufficient Bacteroides fragilis colonies, the production of T regulatory (Treg) cells is limited. Treg cells are responsible for regulating blood pressure. Essentially, we have to correct microbiome dysbiosis to get to the cause of inflammation.6 7
Read more about the microbiome.
What Causes High Blood Pressure – Black Mold Exposure
Black mold, also known as Stachybotrys chartarum, is a type of fungus that thrives in damp environments. It can grow on various surfaces such as walls, ceilings, and floors. When exposed to black mold, it can lead to serious health problems including high blood pressure.
Black mold produces several types of mycotoxins, which are toxic compounds that affect humans and animals. These mycotoxins enter our bodies through inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact. When exposed to these toxins, our body’s immune system goes into overdrive, causing inflammation and an increase in blood pressure.8
When exposed to black mold, our body’s immune system reacts by releasing a chemical called histamine. Histamine is responsible for causing inflammation and other allergic reactions. This release of histamine leads to an increase in blood pressure as it causes the blood vessels to narrow.9
Read more about the toxic effects of mold.
What Causes High Blood Pressure – Mouthwash
Studies have shown that certain ingredients in mouthwash increase blood pressure levels. One study found that people who used mouthwash had a higher risk of developing high blood pressure compared to those who didn’t use it. The reason is because mouthwash interferes with the body’s production of nitric oxide.10
The Link Between Salt And Blood Pressure
Sodium is an essential mineral for our body, but too much of it has negative health effects. Excess sodium causes the body to retain water, increasing blood volume and putting more pressure on the walls of blood vessels. However, there is a stark difference between the blood pressure-increasing effect of refined table salt versus Celtic sea salt.11
Does Celtic Salt Lower Blood Pressure?
Celtic salt is a mineral-rich sea salt. It is harvested from the coastal regions of France and contains trace amounts of minerals such as magnesium, calcium, potassium, and iron.
One of the most commonly asked questions is, does Celtic salt lower blood pressure? A study published in Food & Nutrition Research found that consuming natural sea salt did not induce hypertension to the same extent as refined table salt. One potential reason for this is sea salt’s magnesium content. So while Celtic salt does not lower blood pressure per se, it is a far better option for seasoning food than refined table salt.12
Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure – Magnesium
One key element that has been shown to have a positive effect on blood pressure is magnesium. Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, such as muscle and nerve function, regulating blood sugar levels, and maintaining healthy bones.13 In one study, participants who took magnesium supplements saw a reduction in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure.14
Incorporate more magnesium into your diet by consuming leafy greens like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard. Also consume nuts and seeds such as almonds, cashews, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds. Avocados and fatty fish like salmon and mackerel are also high in magnesium.
Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure – Potassium
Studies have shown that increasing potassium intake is just as beneficial for lowering blood pressure as decreasing sodium intake. This is because potassium helps to counteract the effects of sodium in the body. Adequate intake of potassium, especially when combined with magnesium, has been linked to lower blood pressure and reduced risk of heart disease.15
Foods rich in potassium include fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, and dairy products. Some of the best sources of potassium are bananas, avocados, sweet potatoes, spinach, and white beans.
Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure – Berries
Berries contain high levels of polyphenols, which are antioxidants that reduce inflammation in the body. Blueberries contain anthocyanins, which relax blood vessels and improve blood flow, resulting in lower blood pressure. Cranberries have high levels of antioxidants and polyphenols that reduce inflammation and improve heart health. Strawberries have also been shown to reduce hypertension when consumed regularly. Last, but definitely not least, Hawthorne berries take the cake when it comes to blood pressure reduction.16
Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure – Hawthorne Berries
Hawthorne berries, also known as haws or thorn apples, come from the Crataegus plant. The plant produces small red berries that have been used for centuries in traditional medicine to treat various health conditions.
Hawthorne berries contain flavonoids and procyanidins, which are powerful antioxidants that dilate blood vessels. This allows for better circulation and a decrease in blood pressure. Additionally, hawthorne berries have been shown to improve the strength of heart muscle contractions, making it easier for the heart to pump blood.
Hawthorne berries can be consumed in various forms, including as a tea, tincture, or supplement. It’s important to note that it may take several weeks of consistent use to see a noticeable decrease in blood pressure.17
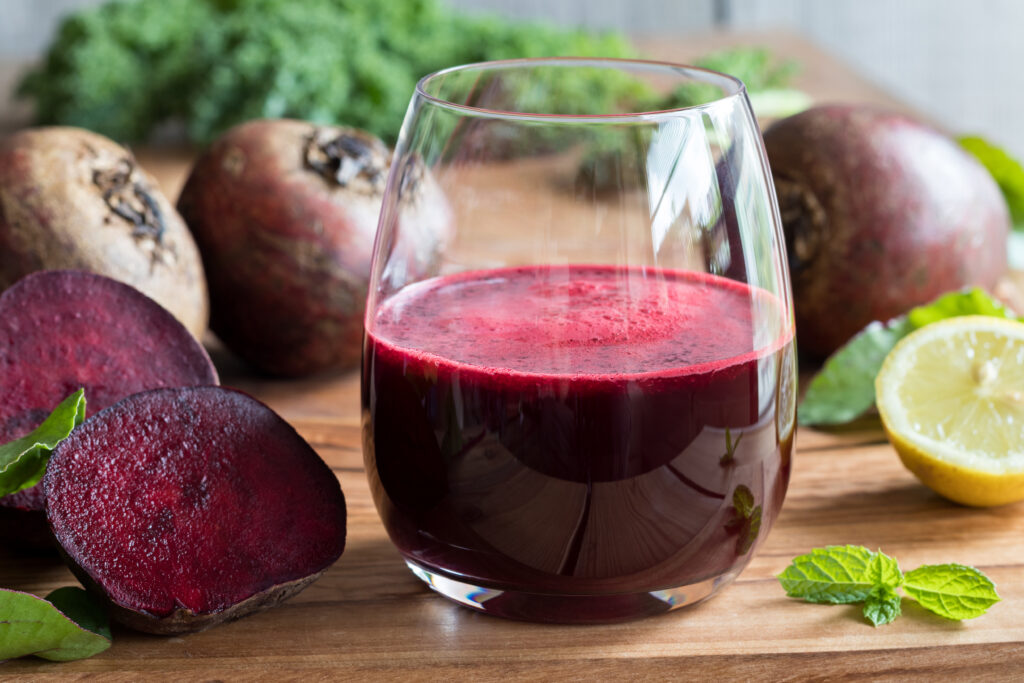
Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure – Beetroot Juice
Beetroot juice is rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and nitrates. Nitrates are compounds found in many plant-based foods, including leafy greens like spinach and arugula, and radishes. When ingested, nitrates are converted into nitric oxide which relaxes and widen blood vessels, counteracting hypertension. To receive the blood pressure-reducing effect of beets, simply drink a glass of fresh beetroot juice each day.18

Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure – Celery Juice
Celery juice has been used in traditional medicine for centuries because it offers a variety of health benefits. Celery is rich in phytochemicals, including phthalides and polyphenols, which reduce hypertension by dilating the blood vessels and reducing inflammation. Additionally, celery contains high levels of potassium. One of the easiest ways to consume celery juice is by juicing fresh stalks of celery. You can also blend it with other fruits and vegetables like beetroot.19
Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure – Ginger
Ginger, a spicy root, is commonly used as a spice in cooking and has been used for its medicinal properties for centuries. Its active ingredients, gingerols and shogaols, have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects that reduce blood pressure. Ginger contains compounds that block calcium channels, preventing them from constricting and increasing blood pressure. Ginger also inhibits the production of angiotensin, helping to keep blood vessels relaxed.
Ginger can easily be added to dishes such as stir-fries, soups, and stews for a spicy kick. Boil sliced ginger in water for about 10 minutes to make a soothing and beneficial tea. Adding a small piece of ginger to your smoothie can give it an extra boost of flavor.20
Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure – Cinnamon
Cinnamon is a well-known spice that has been used for centuries in both culinary and medicinal practices. Cinnamon improves blood flow and circulation, which reduces strain on the heart. In addition, cinnamon contains a compound called cinnamic acid, which has a positive effect on blood pressure levels.21
Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure – Garlic
Studies have shown that garlic can effectively lower blood pressure by dilating blood vessels. It also helps reduce the risk of blood clots, which leads to heart attacks and strokes. Additionally, garlic contains a compound called allicin, which has anti-inflammatory effects.22
Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure – Fatty Fish
Fatty fish are types of fish that contain high levels of omega-3 fatty acids. These essential fatty acids have been shown to have numerous health benefits, including reducing inflammation and promoting heart health. Research has shown that consuming fatty fish regularly lowers blood pressure in individuals with hypertension. Some common types of fatty fish include salmon, mackerel, and sardines.23
Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure – L-Citrulline And L-Arginine
L-citrulline and L-arginine are both non-essential amino acids, meaning that our bodies can produce them on their own. They are also commonly found in foods such as watermelon, pumpkin seeds, and seafood. Studies have shown that both L-citrulline and L-arginine have a positive impact on blood pressure. L-citrulline is converted into L-arginine in the body. This conversion then leads to the production of nitric oxide.24
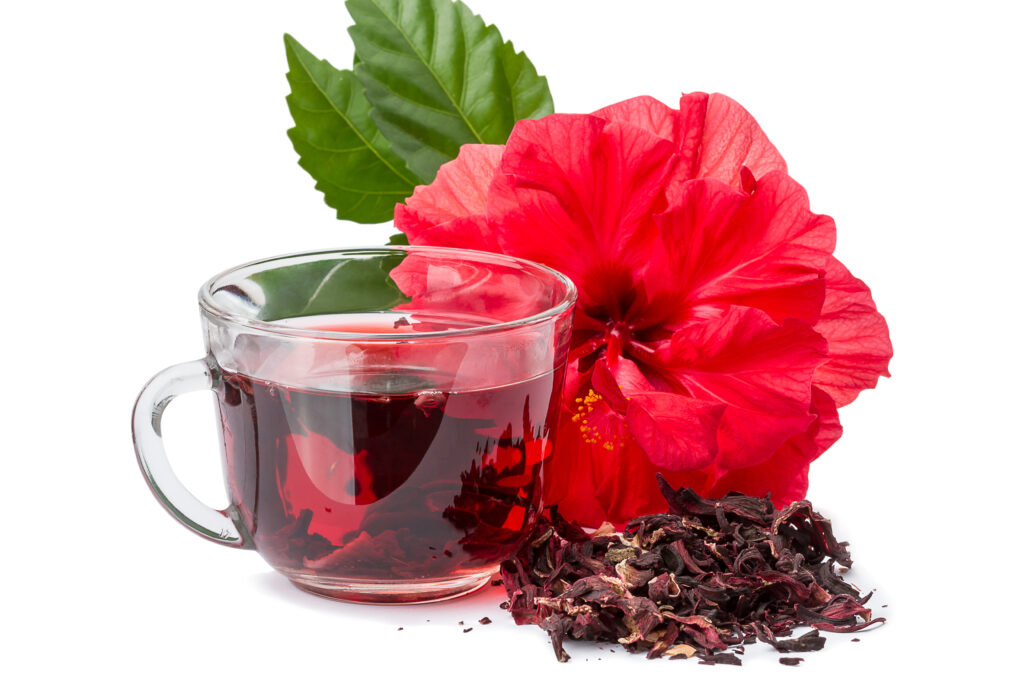
Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure – Hibiscus Tea
Hibiscus tea is an herbal tea made from the dried petals of the hibiscus flower. It is rich in various beneficial compounds such as polyphenols, flavonoids, and anthocyanins, which give hibiscus tea its deep red color. Studies have found that drinking hibiscus tea daily lowers both systolic and diastolic blood pressure.25

Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure – Basil
Basil is a popular herb in the mint family that is commonly used in cooking. Basil contains compounds such as eugenol, rosmarinic acid, and beta-caryophyllene, which have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. These compounds help relax the blood vessels. Basil also contains potassium.26
Fasting Lowers High Blood Pressure
Studies have shown that fasting is an effective way to lower high blood pressure by correcting insulin resistance. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance results in inflammation that damages the walls of the arteries, leading to an increase in blood pressure.27
Read more about the benefits of fasting.
Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure – Other Medicinal Plants
This list of natural ways to lower blood pressure is only the beginning. For more, check out this review, Medicinal Plants in the Treatment of Hypertension.
What Causes High Blood Pressure – Natural Ways To Lower Blood Pressure
Now that you know what causes high blood pressure and natural ways to lower blood pressure, incorporate some or all of these blood pressure-lowering strategies to improve your cardiovascular health.
Read more about inflammation and how to reduce it.
References
1 Singh S, Shankar R, Singh GP. Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Hypertension: A Cross-Sectional Study in Urban Varanasi. Int J Hypertens. 2017;2017:5491838. doi: 10.1155/2017/5491838. Epub 2017 Dec 3. PMID: 29348933; PMCID: PMC5733954.
2 Carey RM, Wright JT Jr, Taler SJ, Whelton PK. Guideline-Driven Management of Hypertension: An Evidence-Based Update. Circ Res. 2021 Apr 2;128(7):827-846. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318083. Epub 2021 Apr 1. PMID: 33793326; PMCID: PMC8034801.
3 Stress and heart health. (2024, February 8). www.heart.org. https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-lifestyle/stress-management/stress-and-heart-health
4 How does sleep affect your heart health? | cdc.gov. (2023, September 6). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
5 Zhang Z, Zhao L, Zhou X, Meng X, Zhou X. Role of inflammation, immunity, and oxidative stress in hypertension: New insights and potential therapeutic targets. Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 10;13:1098725. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1098725. PMID: 36703963; PMCID: PMC9871625.
6 Cheng H, Guan X, Chen D, Ma W. The Th17/Treg Cell Balance: A Gut Microbiota-Modulated Story. Microorganisms. 2019 Nov 20;7(12):583. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7120583. PMID: 31756956; PMCID: PMC6956175.
7 De Miguel C, Rudemiller NP, Abais JM, Mattson DL. Inflammation and hypertension: new understandings and potential therapeutic targets. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2015 Jan;17(1):507. doi: 10.1007/s11906-014-0507-z. PMID: 25432899; PMCID: PMC4418473.
8 Hyvönen S, Lohi J, Tuuminen T. Moist and Mold Exposure is Associated With High Prevalence of Neurological Symptoms and MCS in a Finnish Hospital Workers Cohort. Saf Health Work. 2020 Jun;11(2):173-177. doi: 10.1016/j.shaw.2020.01.003. Epub 2020 Jan 29. PMID: 32596012; PMCID: PMC7303478.
9 Potnuri, A.G., Allakonda, L., Appavoo, A. et al. Association of histamine with hypertension-induced cardiac remodeling and reduction of hypertrophy with the histamine-2-receptor antagonist famotidine compared with the beta-blocker metoprolol. Hypertens Res 41, 1023–1035 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-018-0109-2
10 Joshipura K, Muñoz-Torres F, Fernández-Santiago J, Patel RP, Lopez-Candales A. Over-the-counter mouthwash use, nitric oxide and hypertension risk. Blood Press. 2020 Apr;29(2):103-112. doi: 10.1080/08037051.2019.1680270. Epub 2019 Nov 11. PMID: 31709856; PMCID: PMC7125030.
11 Grillo A, Salvi L, Coruzzi P, Salvi P, Parati G. Sodium Intake and Hypertension. Nutrients. 2019 Aug 21;11(9):1970. doi: 10.3390/nu11091970. PMID: 31438636; PMCID: PMC6770596.
12 Lee BH, Yang AR, Kim MY, McCurdy S, Boisvert WA. Natural sea salt consumption confers protection against hypertension and kidney damage in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Food Nutr Res. 2016 Dec 20;61(1):1264713. doi: 10.1080/16546628.2017.1264713. Erratum in: Food Nutr Res. 2017 Mar 20;61(1):1300375. PMID: 28325999; PMCID: PMC5328355.
13 Chrysant SG, Chrysant GS. Association of hypomagnesemia with cardiovascular diseases and hypertension. Int J Cardiol Hypertens. 2019 Apr 23;1:100005. doi: 10.1016/j.ijchy.2019.100005. PMID: 33447739; PMCID: PMC7803063.
14 Houston M. The role of magnesium in hypertension and cardiovascular disease. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2011 Nov;13(11):843-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2011.00538.x. Epub 2011 Sep 26. PMID: 22051430; PMCID: PMC8108907.
15 Filippini T, Naska A, Kasdagli MI, Torres D, Lopes C, Carvalho C, Moreira P, Malavolti M, Orsini N, Whelton PK, Vinceti M. Potassium Intake and Blood Pressure: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Jun 16;9(12):e015719. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.015719. Epub 2020 Jun 5. PMID: 32500831; PMCID: PMC7429027.
16 Noad RL, Rooney C, McCall D, Young IS, McCance D, McKinley MC, Woodside JV, McKeown PP. Beneficial effect of a polyphenol-rich diet on cardiovascular risk: a randomised control trial. Heart. 2016 Sep 1;102(17):1371-9. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2015-309218. Epub 2016 May 10. PMID: 27164919.
17 Walker AF, Marakis G, Morris AP, Robinson PA. Promising hypotensive effect of hawthorn extract: a randomized double-blind pilot study of mild, essential hypertension. Phytother Res. 2002 Feb;16(1):48-54. doi: 10.1002/ptr.947. PMID: 11807965.
18 Bonilla Ocampo DA, Paipilla AF, Marín E, Vargas-Molina S, Petro JL, Pérez-Idárraga A. Dietary Nitrate from Beetroot Juice for Hypertension: A Systematic Review. Biomolecules. 2018 Nov 2;8(4):134. doi: 10.3390/biom8040134. PMID: 30400267; PMCID: PMC6316347.
19 Illes JD. Blood Pressure Change After Celery Juice Ingestion in a Hypertensive Elderly Male. J Chiropr Med. 2021 Jun;20(2):90-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jcm.2021.04.001. Epub 2021 Jun 16. PMID: 34987326; PMCID: PMC8703128.
20 Hasani H, Arab A, Hadi A, Pourmasoumi M, Ghavami A, Miraghajani M. Does ginger supplementation lower blood pressure? A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Phytother Res. 2019 Jun;33(6):1639-1647. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6362. Epub 2019 Apr 11. PMID: 30972845.
21 Shirzad F, Morovatdar N, Rezaee R, Tsarouhas K, Abdollahi Moghadam A. Cinnamon effects on blood pressure and metabolic profile: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial in patients with stage 1 hypertension. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2021 Jan-Feb;11(1):91-100. PMID: 33628723; PMCID: PMC7885002.
22 Ried K. Garlic lowers blood pressure in hypertensive subjects, improves arterial stiffness and gut microbiota: A review and meta-analysis. Exp Ther Med. 2020 Feb;19(2):1472-1478. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8374. Epub 2019 Dec 27. PMID: 32010325; PMCID: PMC6966103.
23 Tao LY, Wang YR, Zhang YF, Liu P, Chen XH. Does omega-3 lower blood pressure?: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Aug 28;99(35):e21955. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021955. PMID: 32871944; PMCID: PMC7458235.
24 Barkhidarian B, Khorshidi M, Shab-Bidar S, Hashemi B. Effects of L-citrulline supplementation on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2019 Jan-Feb;9(1):10-20. PMID: 30788274; PMCID: PMC6369322.
25 Jalalyazdi M, Ramezani J, Izadi-Moud A, Madani-Sani F, Shahlaei S, Ghiasi SS. Effect of hibiscus sabdariffa on blood pressure in patients with stage 1 hypertension. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2019 Jul-Sep;10(3):107-111. doi: 10.4103/japtr.JAPTR_402_18. PMID: 31334091; PMCID: PMC6621350.
26 Umar A, Imam G, Yimin W, Kerim P, Tohti I, Berké B, Moore N. Antihypertensive effects of Ocimum basilicum L. (OBL) on blood pressure in renovascular hypertensive rats. Hypertens Res. 2010 Jul;33(7):727-30. doi: 10.1038/hr.2010.64. Epub 2010 May 7. PMID: 20448636.
27 Sutton EF, Beyl R, Early KS, Cefalu WT, Ravussin E, Peterson CM. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves Insulin Sensitivity, Blood Pressure, and Oxidative Stress Even without Weight Loss in Men with Prediabetes. Cell Metab. 2018 Jun 5;27(6):1212-1221.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.04.010. Epub 2018 May 10. PMID: 29754952; PMCID: PMC5990470.