How To Fix Leaky Gut And Improve The Microbiome – The Power Of Lifestyle And Diet
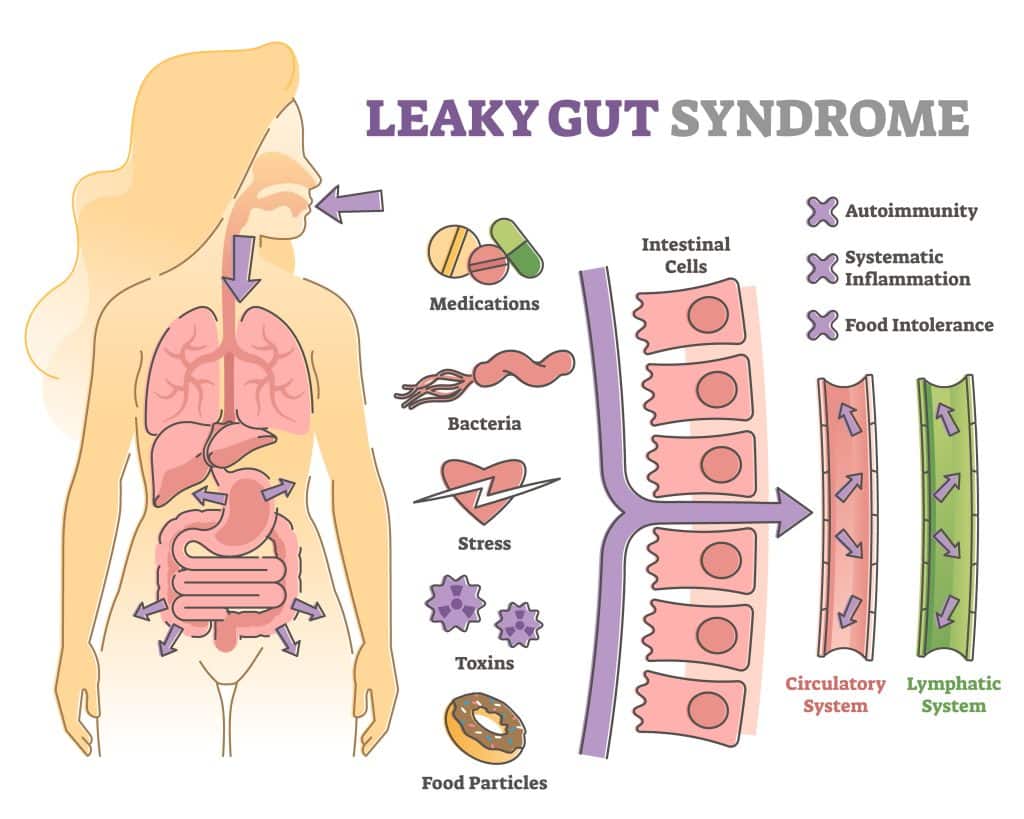
If you can fix leaky gut syndrome, you can put a stop to chronic inflammation and immune system dysfunction. Leaky gut syndrome leads to a variety of symptoms such as bloating, gas, fatigue, joint pain, skin issues, and autoimmune conditions. It is important to note that a leaky gut and an imbalance in the microbiome often go hand in hand. This is because the lining of the gut plays a crucial role in keeping harmful substances out of our bloodstream, while also allowing beneficial nutrients to be absorbed.
When the gut becomes permeable or “leaky,” it means that there are gaps in the intestinal lining that are allowing toxins, bacteria, and other undigested food particles to pass through and enter the bloodstream.1
One of the main causes of leaky gut is an unhealthy balance of bacteria in the gut, also known as dysbiosis. This can occur due to a poor diet high in processed foods and sugar, chronic stress, overuse of antibiotics, and other environmental factors. When there is an overgrowth of harmful bacteria and a depletion of beneficial bacteria, it can lead to inflammation in the gut lining and contribute to leaky gut.2
How To Fix Leaky Gut – Manage Stress Levels
Chronic stress can have a negative impact on the microbiome and contribute to leaky gut. Incorporate stress-reducing activities into your daily routine, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.3
The Connection Between Leaky Gut And GMOs
GMOs, or genetically modified organisms, refer to plants or animals that have been genetically altered using biotechnology. This involves inserting DNA from one organism into another to create a desired characteristic, such as resistance to pests or herbicides. The use of GMOs in agriculture has become increasingly common in recent years, with most processed foods containing at least one GMO ingredient.
While the long-term effects of consuming GMOs are still being studied, there have been concerns raised about their potential impact on gut health. One of the main concerns is that GMOs disrupt the delicate balance of bacteria in our gut.4
Research has shown that consuming GMOs can have negative effects on the gut. A study found that rats fed a diet containing genetically modified maize had significant damage to their intestinal lining and changes in their gut bacteria.5 Another study found that rats fed a diet containing genetically modified soy had an increased risk of developing leaky gut.6
One potential reason for the negative effects of GMOs on gut health could be the presence of glyphosate, a herbicide commonly used in conjunction with GMO crops. Glyphosate has been linked to disruptions in the gut microbiome and increased intestinal permeability.

The Connection Between Leaky Gut And Glyphosate
Glyphosate is an herbicide commonly used in agriculture and gardening to kill weeds. It is the active ingredient in popular products such as Roundup, and its use has increased dramatically since the introduction of genetically modified crops that are resistant to it.
Studies have shown that glyphosate disrupts the balance of gut bacteria. Glyphosate has been found to specifically target beneficial bacteria while allowing harmful bacteria to thrive, leading to an imbalance in the microbiome. This disruption can weaken the intestinal barrier and contribute to leaky gut.7
Additionally, glyphosate has been shown to have a direct toxic effect on intestinal cells. It can damage the tight junctions between cells that form the lining of the intestine, further compromising its integrity and allowing unwanted substances to enter the bloodstream. Glyphosate has also been linked to numerous other health issues including autoimmune diseases, and neurological disorders.8
To protect ourselves from glyphosate exposure we must choose organic produce and products whenever possible. Organic farming prohibits the use of synthetic pesticides and herbicides, including glyphosate. By choosing organic, we can limit our exposure to this potentially harmful chemical.
Read more about the toxic effects of glyphosate.
The Connection Between Leaky Gut And Sucralose
One cause of leaky gut is the consumption of artificial sweeteners, particularly sucralose, according to a 2023 study.9 Sucralose is a commonly used sugar substitute in many processed foods and beverages. It is marketed as a calorie-free alternative to sugar, making it appealing for people looking to reduce their sugar intake.
In addition to causing leaky gut syndrome, sucralose has also been linked to other health problems such as weight gain, insulin resistance, and disrupted blood sugar levels. These effects can further contribute to digestive issues and increase the risk of developing various chronic diseases.10
How To Fix Leaky Gut – Follow An Anti-inflammatory Diet
Eliminate processed foods, sugar, gluten, and other inflammatory foods while focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, grass-fed meat, omega-3 rich fish, and healthy fats.
Read more about eating an anti-inflammatory diet.
How To Fix Leaky Gut And Improve The Microbiome – The Power Of Glutamine Rich Foods
There are simple ways to improve the health of our gut and combat leaky gut syndrome. One effective method is by consuming glutamine-rich foods. The connection between glutamine and leaky gut has been a topic of interest for many researchers in recent years.
Glutamine is an amino acid that plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the intestinal lining. Glutamine works by promoting the growth and regeneration of intestinal cells, strengthening the tight junctions between them, and enhancing immune function. In other words, glutamine reduces the space between intestinal cells, thereby reducing or eliminating the leakage.11
Glutamine also helps repair and rebuild damaged cells in the digestive tract, making it an essential nutrient for gut health. Glutamine also supports the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which is crucial for a healthy microbiome. It is also an essential nutrient for the proper functioning of the immune system.12
Anyone who wants to fix leaky gut syndrome should start by incorporating more glutamine-rich foods in their diet. Here are some foods high in glutamine.

How To Fix Leaky Gut With Bone Broth
Bone broth is made by simmering bones and connective tissues, which are rich in glutamine. Consuming bone broth regularly can help heal the gut lining and improve overall digestive health.13
Bone broth has been gaining popularity in recent years as a superfood with numerous health benefits. One of the key benefits of bone broth is its high collagen content. Collagen is a protein that is found in our bones, skin, muscles, and tendons. As we age, our natural collagen production decreases, leading to wrinkles, joint pain, and weaker bones. Consuming bone broth can help increase our collagen levels and improve the appearance of our skin, hair, and nails.
In addition to collagen, bone broth also contains amino acids, gelatin, and minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus. These nutrients play important roles in maintaining strong bones and teeth, promoting healthy digestion and gut health, and supporting a strong immune system.
Another benefit of bone broth is its anti-inflammatory properties. The amino acids found in bone broth can help reduce inflammation in the body, which is linked to chronic diseases such as heart disease, and arthritis. By incorporating bone broth into your diet, you may be able to reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
Bone broth has also been shown to support joint health. The gelatin found in bone broth can help strengthen bones, cartilage, and tendons, which can alleviate joint pain and stiffness. This makes bone broth a great option for those with conditions such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.14
Read more about rheumatoid arthritis.
In addition to its physical benefits, bone broth can also have positive effects on mental health. The glycine found in bone broth has been shown to promote relaxation and improve sleep quality. It may also help improve memory and cognitive function.15
How To Fix Leaky Gut With Grass-Fed Meat
Grass-fed red meat is rich in essential nutrients such as glutamine and omega-3 fatty acids, which help reduce inflammation and support gut health. It also contains conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), a type of healthy fat that has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties and aid in healing the gut lining. In addition, grass-fed red meat is a great source of iron and zinc, two important minerals that are commonly deficient in many people’s diets.16
Grass-fed red meat also has a much higher concentration of antioxidants compared to grain-fed meat. Antioxidants help protect the body from damage caused by free radicals and have been linked to decreased risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease. Grass-fed red meat is also a rich source of B vitamins, including B12 which is essential for nerve function and energy production.

How To Fix Leaky Gut With Fermented Foods
Fermented foods include kimchi, sauerkraut, kefir, and yogurt, all of which contain beneficial probiotics that support a healthy microbiome. Fermented cabbage contained in sauerkraut and kimchi is extremely high in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory phytochemicals.17
Fermented foods are not only beneficial for our gut health but also for our immune system. The probiotics found in fermented foods can help strengthen the immune system by increasing the production of white blood cells and improving their function. This can help defend the body against harmful bacteria and viruses.18
In addition, fermented foods can also play a role in reducing inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation has been linked to various health problems such as heart disease. The probiotics found in fermented foods can aid in balancing the gut microbiome, which is essential for maintaining a healthy immune response and reducing inflammation.19

How To Fix Leaky Gut With Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar (ACV) is made from fermented apples and has been used for centuries as a traditional medicine. It contains beneficial enzymes, probiotics, and acetic acid, which can help improve digestion and promote a healthy gut microbiome. Apple cider vinegar has been shown to have numerous health benefits, including its ability to support a healthy gut.
ACV balances pH levels helping to restore balance to the gut environment, which is essential for proper digestion and absorption of nutrients. ACV contains probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that help maintain a healthy gut microbiome. These microorganisms aid in breaking down food, fighting off harmful bacteria, and promoting a strong immune system. The acetic acid in ACV has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation in the gut and ease symptoms of leaky gut syndrome.20
How To Fix Leaky Gut And Improve The Microbiome – The Power Of Lifestyle And Diet
By eating properly and making lifestyle changes, you can fix leaky gut and improve the balance of bacteria in your microbiome. It’s important to note that removing the source of leaky gut is key and that healing takes time and consistency.
Read more about how the microbiome influences autoimmune diseases.
References
1 Paray BA, Albeshr MF, Jan AT, Rather IA. Leaky Gut and Autoimmunity: An Intricate Balance in Individuals Health and the Diseased State. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 21;21(24):9770. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249770. PMID: 33371435; PMCID: PMC7767453.
2 Camilleri M. Leaky gut: mechanisms, measurement and clinical implications in humans. Gut. 2019 Aug;68(8):1516-1526. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318427. Epub 2019 May 10. PMID: 31076401; PMCID: PMC6790068.
3 Karl JP, Margolis LM, Madslien EH, Murphy NE, Castellani JW, Gundersen Y, Hoke AV, Levangie MW, Kumar R, Chakraborty N, Gautam A, Hammamieh R, Martini S, Montain SJ, Pasiakos SM. Changes in intestinal microbiota composition and metabolism coincide with increased intestinal permeability in young adults under prolonged physiological stress. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017 Jun 1;312(6):G559-G571. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00066.2017. Epub 2017 Mar 23. PMID: 28336545.
4 Bawa AS, Anilakumar KR. Genetically modified foods: safety, risks and public concerns-a review. J Food Sci Technol. 2013 Dec;50(6):1035-46. doi: 10.1007/s13197-012-0899-1. Epub 2012 Dec 19. PMID: 24426015; PMCID: PMC3791249.
5 Seralini, GE. Update on long-term toxicity of agricultural GMOs tolerant to roundup. Environ Sci Eur 32, 18 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-020-0296-8
6 Aris A, Leblanc S. Maternal and fetal exposure to pesticides associated to genetically modified foods in Eastern Townships of Quebec, Canada. Reprod Toxicol. 2011 May;31(4):528-33. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2011.02.004. Epub 2011 Feb 18. PMID: 21338670.
7 Lehman PC, Cady N, Ghimire S, Shahi SK, Shrode RL, Lehmler HJ, Mangalam AK. Low-dose glyphosate exposure alters gut microbiota composition and modulates gut homeostasis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2023 Jun;100:104149. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2023.104149. Epub 2023 May 15. PMID: 37196884; PMCID: PMC10330715.
8 Costas-Ferreira C, Durán R, Faro LRF. Toxic Effects of Glyphosate on the Nervous System: A Systematic Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 21;23(9):4605. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094605. PMID: 35562999; PMCID: PMC9101768.
9 Susan S. Schiffman, Elizabeth H. Scholl, Terrence S. Furey & H. Troy Nagle (2023) Toxicological and pharmacokinetic properties of sucralose-6-acetate and its parent sucralose: in vitro screening assays, Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part B, DOI: 10.1080/10937404.2023.2213903
10 Risdon S, Battault S, Romo-Romo A, Roustit M, Briand L, Meyer G, Almeda-Valdes P, Walther G. Sucralose and Cardiometabolic Health: Current Understanding from Receptors to Clinical Investigations. Adv Nutr. 2021 Jul 30;12(4):1500-1513. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmaa185. PMID: 33578411; PMCID: PMC8321845.
11 Rao R, Samak G. Role of Glutamine in Protection of Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junctions. J Epithel Biol Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;5(Suppl 1-M7):47-54. doi: 10.2174/1875044301205010047. PMID: 25810794; PMCID: PMC4369670.
12 Cruzat V, Macedo Rogero M, Noel Keane K, Curi R, Newsholme P. Glutamine: Metabolism and Immune Function, Supplementation and Clinical Translation. Nutrients. 2018 Oct 23;10(11):1564. doi: 10.3390/nu10111564. PMID: 30360490; PMCID: PMC6266414.
13 Mar-Solís LM, Soto-Domínguez A, Rodríguez-Tovar LE, Rodríguez-Rocha H, García-García A, Aguirre-Arzola VE, Zamora-Ávila DE, Garza-Arredondo AJ, Castillo-Velázquez U. Analysis of the Anti-Inflammatory Capacity of Bone Broth in a Murine Model of Ulcerative Colitis. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Oct 20;57(11):1138. doi: 10.3390/medicina57111138. PMID: 34833355; PMCID: PMC8618064.
14 León-López A, Morales-Peñaloza A, Martínez-Juárez VM, Vargas-Torres A, Zeugolis DI, Aguirre-Álvarez G. Hydrolyzed Collagen-Sources and Applications. Molecules. 2019 Nov 7;24(22):4031. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224031. PMID: 31703345; PMCID: PMC6891674.
15 File SE, Fluck E, Fernandes C. Beneficial effects of glycine (bioglycin) on memory and attention in young and middle-aged adults. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1999 Dec;19(6):506-12. doi: 10.1097/00004714-199912000-00004. PMID: 10587285.
16 Daley CA, Abbott A, Doyle PS, Nader GA, Larson S. A review of fatty acid profiles and antioxidant content in grass-fed and grain-fed beef. Nutr J. 2010 Mar 10;9:10. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-9-10. PMID: 20219103; PMCID: PMC2846864.
17 Rokayya S, Li CJ, Zhao Y, Li Y, Sun CH. Cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata) phytochemicals with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014 Jan;14(11):6657-62. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.11.6657. PMID: 24377584.
18 Wastyk HC, Fragiadakis GK, Perelman D, Dahan D, Merrill BD, Yu FB, Topf M, Gonzalez CG, Van Treuren W, Han S, Robinson JL, Elias JE, Sonnenburg ED, Gardner CD, Sonnenburg JL. Gut-microbiota-targeted diets modulate human immune status. Cell. 2021 Aug 5;184(16):4137-4153.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.06.019. Epub 2021 Jul 12. PMID: 34256014; PMCID: PMC9020749.
19 Shahbazi R, Sharifzad F, Bagheri R, Alsadi N, Yasavoli-Sharahi H, Matar C. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Properties of Fermented Plant Foods. Nutrients. 2021 Apr 30;13(5):1516. doi: 10.3390/nu13051516. PMID: 33946303; PMCID: PMC8147091.
20 Tripathi S, Mitra Mazumder P. Comprehensive investigations for a potential natural prophylaxis-A cellular and murine model for apple cider vinegar against hydrogen peroxide and scopolamine induced oxidative stress. Drug Dev Res. 2022 Feb;83(1):105-118. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21849. Epub 2021 Jun 28. PMID: 34184291.




