Should I Take Collagen – Health Benefits Of Collagen Supplementation
The question I get asked all the time is, “Should I take collagen?” It’s time I answered that question in detail. Collagen is the most abundant protein in our body, making up about 30% of our total protein content. It is found in the skin, bones, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Collagen plays a crucial role in maintaining the structure and strength of connective tissues.1
Should I Take Collagen As I Age?
The production of collagen decreases as we age, leading to wrinkles, joint pain, and stiffness. This is why many people turn to collagen supplements to improve their overall health and appearance.2
Should I Take Collagen – Joint Health
Collagen plays a vital role in maintaining the health of our joints. It acts as a cushion between bones, providing them with support and flexibility. As we age, the collagen in our joints starts to degrade, leading to joint pain and stiffness. Studies have shown that taking collagen supplements can help improve joint pain and mobility in people with osteoarthritis.3
Should I Take Collagen – Skin Health
Collagen is responsible for maintaining the elasticity and hydration of our skin. As we age, less collagen leads to visible signs of aging such as wrinkles, dryness, and saggy skin. By consuming collagen, you can boost the production of collagen in your body, resulting in smoother, firmer, and more hydrated skin.4

Should I Take Collagen – Muscle Function
Collagen is not only found in our skin and bones but also in our muscles. It is a crucial component for muscle strength and function. As we age, our muscle mass naturally decreases, and this can lead to weakness and loss of mobility. Studies have shown that collagen supplementation can help increase muscle mass and strength, especially when combined with resistance training.5
Should I Take Collagen – Bone Strength
Collagen is a crucial component of our bones, making up around 90% of the organic components. It provides structure and strength to our bones, helping them to resist fractures and maintain their density. As we age, our bone density decreases, increasing the risk of osteoporosis. Taking collagen supplements can help maintain bone density and reduce the risk of bone fractures.6
Should I Take Collagen – Hair And Nails
Not only does collagen benefit our skin and muscles, but it also has a positive impact on our hair and nails. Collagen is an important building block for our hair and nails, providing them with strength and structure. Taking collagen supplements can help improve the strength and appearance of brittle nails and thinning hair.7
Should I Take Collagen – Gut Health
Collagen is essential for maintaining a healthy gut lining. It helps to seal and heal the digestive tract, preventing toxins from entering our bloodstream. Studies have shown that collagen supplementation can help improve various digestive issues such as leaky gut syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease.8
Read more about the importance of gut health.
Should I Take Collagen With Protein-Rich Foods
Consuming protein-rich foods increases collagen levels in our body. This is because protein-rich foods contain amino acids, the building blocks of protein, which help support collagen production.9
Fish and grass-fed meats are excellent sources of protein. These foods contain high amounts of lysine, glycine, and proline, three essential amino acids that support collagen production.10 11 Fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and amino acids that stimulate collagen production.12
Almonds, walnuts, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds are all good sources of protein. They also provide vitamin E, which helps protect the skin from oxidative damage.13
Should I Take Collagen With Vitamin C
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin that has many important functions in the body. It is essential for the production of collagen, as it helps in the conversion of proline to hydroxyproline and lysine to hydroxylysine. Without sufficient vitamin C, collagen production is affected, leading to weakened connective tissues.14
Vitamin C acts as an antioxidant and helps protect these enzymes from damage, ensuring that collagen production can proceed smoothly.
In addition to its role in collagen production, vitamin C also helps to maintain the health of existing collagen in the body. It does this by preventing the breakdown of collagen fibers due to oxidative stress. This is important as collagen can become damaged over time, leading to loss of elasticity and strength in the skin and other tissues.15
Furthermore, vitamin C also aids in wound healing by promoting collagen synthesis at the site of injury. It helps to increase blood flow to the wounded area, which brings nutrients and oxygen necessary for collagen production. Vitamin C also has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce swelling and promote a faster healing process.16
Berries such as strawberries, blueberries, and blackberries are not only delicious but also packed with vitamin C and antioxidants. Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and collard greens are excellent sources of vitamin C. Citrus fruits like oranges and lemons are also high in vitamin C, making them another great option for promoting collagen production.17
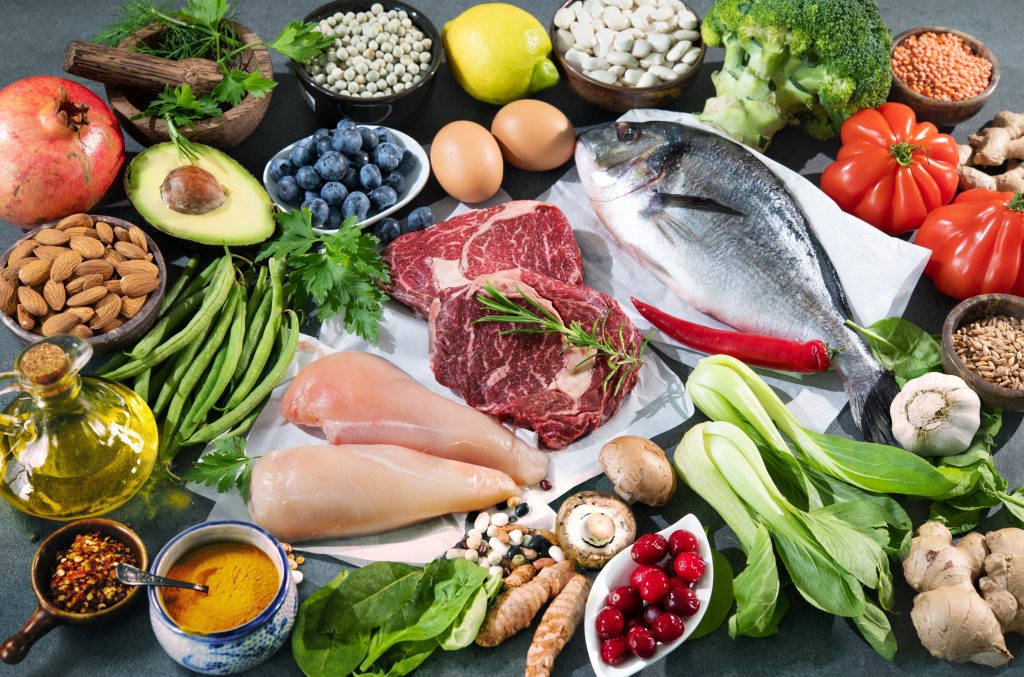

Should I Take Collagen With Foods Rich In Sulfur, Copper, Biotin, Zinc, And Silica
Garlic and onions are flavorful additions to meals and also contain sulfur, a mineral that is essential for collagen production.18
Beans, lentils, and other legumes are rich in protein and also contain copper, a mineral that is essential for collagen production.19
Biotin, also known as vitamin B7, is essential for maintaining healthy hair, skin, and nails. It works by helping our bodies break down amino acids, which are the building blocks of collagen. Consuming biotin-rich food alongside collagen can promote hair growth, improve skin elasticity, and strengthen brittle nails. Foods high in biotin include eggs, nuts, seeds, liver, avocados, broccoli, and mushrooms.20
Zinc is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in collagen production. It helps activate enzymes involved in the synthesis of collagen, making it an important nutrient to consider when taking collagen supplements. Additionally, zinc also has antioxidant properties that can protect collagen from damage and support overall skin health. Foods high in zinc include shellfish like oysters and shrimp, seeds, nuts, and meat.21
Silica is a trace mineral that helps maintain healthy connective tissues, including collagen. Consuming silica-rich foods alongside collagen can help improve skin elasticity and hydration, as well as promote hair and nail growth. Foods high in silica include green beans and leafy greens.22
Read more about how your diet can improve your health.
What Is Hydrolyzed Collagen?
Hydrolyzed collagen, also known as collagen hydrolysate or collagen peptides, is a type of protein that has been broken down into smaller amino acid chains through a process called hydrolysis. This results in a form of collagen that is easier for our bodies to absorb and utilize.
Hydrolyzed collagen is derived from natural sources such as marine (fish), bovine (cow), and porcine (pig) collagen. Hydrolyzed collagen is free from dairy, gluten, and other common allergens, making it suitable for those with dietary restrictions.
One of the key advantages of hydrolyzed collagen is its ability to be easily digested and absorbed by the body. This is due to the smaller amino acid chains, which can enter the bloodstream more quickly and efficiently compared to whole proteins. As a result, hydrolyzed collagen has a higher bioavailability, meaning that a larger proportion of the ingested collagen is able to reach target tissues and provide benefits.23

Benefits Of Marine Collagen Supplements
Marine collagen supplements have become increasingly popular in recent years due to the numerous benefits they provide. Marine collagen is derived from fish scales and skin. Marine collagen is a type I collagen, which means it is the most abundant form of collagen in our bodies. It is found in our skin, bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and other connective tissues.24
Benefits Of Bovine Collagen Supplements
Grass-fed organic bovine collagen supplements are derived from the hides and bones of cows that have been raised on a natural diet of grass. Unlike conventional cows that are fed grains or soy-based feed, grass-fed cows consume a natural diet that is free from harmful chemicals and hormones. This results in a higher-quality collagen product, making it the only choice for health enthusiasts.
Bovine collagen consists of larger particles compared to marine collagen. Bovine collagen supplements are usually preferred over marine collagen supplements because they are composed of type I and III collagen, which are both required by our bodies.25
Benefits Of Porcine Collagen Supplements
Porcine collagen supplements are derived from the skin, bones, and tendons of pigs. They are a rich source of type I and type III collagen like bovine collagen. Porcine collagen is ideal for improving bone health.26
Should I Take Collagen – Health Benefits Of Collagen Supplementation
Taking collagen has proven to have numerous health benefits. From improving skin elasticity and reducing joint pain, to promoting heart health and boosting muscle mass, collagen supplementation can greatly benefit overall health and well-being.
However, it is important to note that the effectiveness of collagen supplements may vary from person to person. Additionally, it is also important to make sure that the collagen supplement being taken is from a reputable source and has undergone proper testing and certification.
Overall, while taking collagen can have many positive effects on the body, it should not be viewed as a cure-all solution. Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle are still key factors in achieving optimal health. However, incorporating collagen supplementation is a beneficial addition to one’s overall wellness routine.
Read more about eating a healthy, anti-inflammatory diet.
References
1 Wu M, Cronin K, Crane JS. Biochemistry, Collagen Synthesis. [Updated 2023 Sep 4]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507709/
2 Al-Atif H. Collagen Supplements for Aging and Wrinkles: A Paradigm Shift in the Fields of Dermatology and Cosmetics. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2022 Jan 1;12(1):e2022018. doi: 10.5826/dpc.1201a18. PMID: 35223163; PMCID: PMC8824545.
3 Khatri M, Naughton RJ, Clifford T, Harper LD, Corr L. The effects of collagen peptide supplementation on body composition, collagen synthesis, and recovery from joint injury and exercise: a systematic review. Amino Acids. 2021 Oct;53(10):1493-1506. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-03072-x. Epub 2021 Sep 7. PMID: 34491424; PMCID: PMC8521576.
4 de Miranda RB, Weimer P, Rossi RC. Effects of hydrolyzed collagen supplementation on skin aging: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Dermatol. 2021 Dec;60(12):1449-1461. doi: 10.1111/ijd.15518. Epub 2021 Mar 20. PMID: 33742704.
5 Zdzieblik D, Oesser S, Baumstark MW, Gollhofer A, König D. Collagen peptide supplementation in combination with resistance training improves body composition and increases muscle strength in elderly sarcopenic men: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Nutr. 2015 Oct 28;114(8):1237-45. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515002810. Epub 2015 Sep 10. PMID: 26353786; PMCID: PMC4594048.
6 Viguet-Carrin S, Garnero P, Delmas PD. The role of collagen in bone strength. Osteoporos Int. 2006;17(3):319-36. doi: 10.1007/s00198-005-2035-9. Epub 2005 Dec 9. PMID: 16341622.
7 Wang H. A Review of the Effects of Collagen Treatment in Clinical Studies. Polymers (Basel). 2021 Nov 9;13(22):3868. doi: 10.3390/polym13223868. PMID: 34833168; PMCID: PMC8620403.
8 Chen Q, Chen O, Martins IM, Hou H, Zhao X, Blumberg JB, Li B. Collagen peptides ameliorate intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in immunostimulatory Caco-2 cell monolayers via enhancing tight junctions. Food Funct. 2017 Mar 22;8(3):1144-1151. doi: 10.1039/c6fo01347c. PMID: 28174772.
9 Paul C, Leser S, Oesser S. Significant Amounts of Functional Collagen Peptides Can Be Incorporated in the Diet While Maintaining Indispensable Amino Acid Balance. Nutrients. 2019 May 15;11(5):1079. doi: 10.3390/nu11051079. PMID: 31096622; PMCID: PMC6566836.
10 Yamauchi M, Sricholpech M. Lysine post-translational modifications of collagen. Essays Biochem. 2012;52:113-33. doi: 10.1042/bse0520113. PMID: 22708567; PMCID: PMC3499978.
11 de Paz-Lugo P, Lupiáñez JA, Meléndez-Hevia E. High glycine concentration increases collagen synthesis by articular chondrocytes in vitro: acute glycine deficiency could be an important cause of osteoarthritis. Amino Acids. 2018 Oct;50(10):1357-1365. doi: 10.1007/s00726-018-2611-x. Epub 2018 Jul 13. PMID: 30006659; PMCID: PMC6153947.
12 Hankenson KD, Watkins BA, Schoenlein IA, Allen KG, Turek JJ. Omega-3 fatty acids enhance ligament fibroblast collagen formation in association with changes in interleukin-6 production. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 2000 Jan;223(1):88-95. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1373.2000.22312.x. PMID: 10632966.
13 Bolke L, Schlippe G, Gerß J, Voss W. A Collagen Supplement Improves Skin Hydration, Elasticity, Roughness, and Density: Results of a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Blind Study. Nutrients. 2019 Oct 17;11(10):2494. doi: 10.3390/nu11102494. PMID: 31627309; PMCID: PMC6835901.
14 Boyera N, Galey I, Bernard BA. Effect of vitamin C and its derivatives on collagen synthesis and cross-linking by normal human fibroblasts. Int J Cosmet Sci. 1998 Jun;20(3):151-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1467-2494.1998.171747.x. PMID: 18505499.
15 Bechara N, Flood VM, Gunton JE. A Systematic Review on the Role of Vitamin C in Tissue Healing. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Aug 19;11(8):1605. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081605. PMID: 36009324; PMCID: PMC9405326.
16 DePhillipo NN, Aman ZS, Kennedy MI, Begley JP, Moatshe G, LaPrade RF. Efficacy of Vitamin C Supplementation on Collagen Synthesis and Oxidative Stress After Musculoskeletal Injuries: A Systematic Review. Orthop J Sports Med. 2018 Oct 25;6(10):2325967118804544. doi: 10.1177/2325967118804544. PMID: 30386805; PMCID: PMC6204628.
17 Fenech M, Amaya I, Valpuesta V, Botella MA. Vitamin C Content in Fruits: Biosynthesis and Regulation. Front Plant Sci. 2019 Jan 24;9:2006. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.02006. PMID: 30733729; PMCID: PMC6353827.
18 Huang Y, Shen Z, Chen Q, Huang P, Zhang H, Du S, Geng B, Zhang C, Li K, Tang C, Du J, Jin H. Endogenous sulfur dioxide alleviates collagen remodeling via inhibiting TGF-β/Smad pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 14;6:19503. doi: 10.1038/srep19503. PMID: 26762477; PMCID: PMC4725894.
19 Harris ED, Rayton JK, Balthrop JE, DiSilvestro RA, Garcia-de-Quevedo M. Copper and the synthesis of elastin and collagen. Ciba Found Symp. 1980;79:163-82. doi: 10.1002/9780470720622.ch9. PMID: 6110524.
20 Lim CJ, Jeon JE, Jeong SK, Yoon SJ, Kwon SD, Lim J, Park K, Kim DY, Ahn JK, Kim BW. Growth hormone-releasing peptide-biotin conjugate stimulates myocytes differentiation through insulin-like growth factor-1 and collagen type I. BMB Rep. 2015 Sep;48(9):501-6. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2015.48.9.258. PMID: 25644636; PMCID: PMC4641233.
21 Tengrup I, Ahonen J, Zederfeldt B. Influence of zinc on synthesis and the accumulation of collagen in early granulation tissue. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1981 Mar;152(3):323-6. PMID: 7466582.
22 Calomme MR, Vanden Berghe DA. Supplementation of calves with stabilized orthosilicic acid. Effect on the Si, Ca, Mg, and P concentrations in serum and the collagen concentration in skin and cartilage. Biol Trace Elem Res. 1997 Feb;56(2):153-65. doi: 10.1007/BF02785389. PMID: 9164661.
23 Martínez-Puig D, Costa-Larrión E, Rubio-Rodríguez N, Gálvez-Martín P. Collagen Supplementation for Joint Health: The Link between Composition and Scientific Knowledge. Nutrients. 2023 Mar 8;15(6):1332. doi: 10.3390/nu15061332. PMID: 36986062; PMCID: PMC10058045.
24 Geahchan S, Baharlouei P, Rahman A. Marine Collagen: A Promising Biomaterial for Wound Healing, Skin Anti-Aging, and Bone Regeneration. Mar Drugs. 2022 Jan 10;20(1):61. doi: 10.3390/md20010061. PMID: 35049916; PMCID: PMC8780088.
25 Lupu MA, Gradisteanu Pircalabioru G, Chifiriuc MC, Albulescu R, Tanase C. Beneficial effects of food supplements based on hydrolyzed collagen for skin care (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2020 Jul;20(1):12-17. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8342. Epub 2019 Dec 17. PMID: 32508986; PMCID: PMC7271718.
26 Lingyu Zhu, Yingying Xie, Boting Wen, Mengliang Ye, Yusi Liu, Khandaker Md Sharif Uddin Imam, Huimei Cai, Chunhui Zhang, Fengzhong Wang, Fengjiao Xin,Porcine bone collagen peptides promote osteoblast proliferation and differentiation by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, Journal of Functional Foods, Volume 64, 2020, 103697, ISSN 1756-4646, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2019.103697.